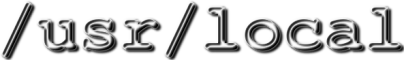docs:tips_n_tricks:ssh.html
This is an old revision of the document!
Table of Contents
SSH
Reverse SSH Tunnel
Imagine you need access from a remote system to a local system, that is allowed to open ssh sessions to the remote system, but the remote system is not allowed to access your local services. This can be solved by using ssh tunnels.
To enable access to a service on port 389 on a local system for the remote system client, open an ssh tunnel to the remote system by
ssh -R 10389:localhost:389 -f -N client
Now, you can access the local service on localhost:10389 on the remote system.
List Fingerprints
To verify the keys in your .ssh/authorized_key file, you can list the fingerprints by:
ssh-keygen -l -f .ssh/authorized_keys
Lock Keys in Agent on Mac OS X (maybe BSD)
eval `SSH_ASKPASS=/usr/local/bin/ssh_askpass.sh ssh-agent` ssh-add -c [keyfile] ssh -A <remote-host>
/usr/local/bin/ssh_askpass.sh:
#! /bin/sh exec xmessage -buttons 'Yes:0,No:1' "$@"
docs/tips_n_tricks/ssh.html.1316780880.txt.gz · Last modified: 23.09.2011 14:28 CEST by peter